Canvas Architecture
About Canvas
Canvas is the name we use for our tech platform. We feel that we have identified a few core concepts that can support a number of use cases and we have built these concepts into Canvas. The concept, which you will hear described as Activity Based Credit from time to time by Nick our CEO, has three main components:
Accounts - supporting accounts, currencies, transactions and account entries - much like a standard bank account system.Seriv
Entities - supporting different types of entities, such as Suppliers, Customers, Supply Partners, Service Providers. Entities, can have 1 => many Projects.
Activity - Canvas records activity from a number of sources, which we aggregate into our accounting system. Activity is created by Assets and an asset can be anything from a Solar Water Pump, to an area of forestry.
Canvas Use Cases
We currently support two use cases on our Canvas platform:
CaVEx - Our carbon value exchange, which monitors and creates Carbon Credits from a variety of Assets, making these available to customers via our Customer facing application.
Daylipa - PAYG Solar Water Pumps, we monitor and control solar water pumps so that users can participate in a Pay as You Go contract.
Protecting Canvas
So far having Canvas as a shared platform has provided a great deal of benefit to us, but it is important that we protect it, keeping it a simple as possible and not over burden it by adding edge case functionality. Canvas needs to stick to the core concepts outlined above, and ancillary functionality should be built separately to keep our core code base clean. Edge case functionality can be added using satelite apps which can consume the back end services.
Architecture
Canvas comprises a suite of Angular Apps, Web API's, internal GRPC services, Databases and background tasks. We have been using C4 diagrams to describe our architecture as shown below:
Canvas System Context Diagram
As you can see from the high level diagram below, the Canvas system is split into 3 main parts:
Data Ingestion - responsible for receiving and storing incoming data from the IOT hubs(s) and project API(s). Within this application (and Azure building blocks), we are expecting to perform some aggregation, anomoly detection and audit. This will most likely be achieved using Azure tools such as
Stream Analytics.Canvas Core - provides core functionality that can be used across multiple use cases, including Account/Transaction management, Activity recording, Asset and Customer management, Billing, Payments...
Cavex Customer - this is only used in the CaVEx use case, this provides web and Mobile App functionality for Project owners and Carbon Credit Buyers.
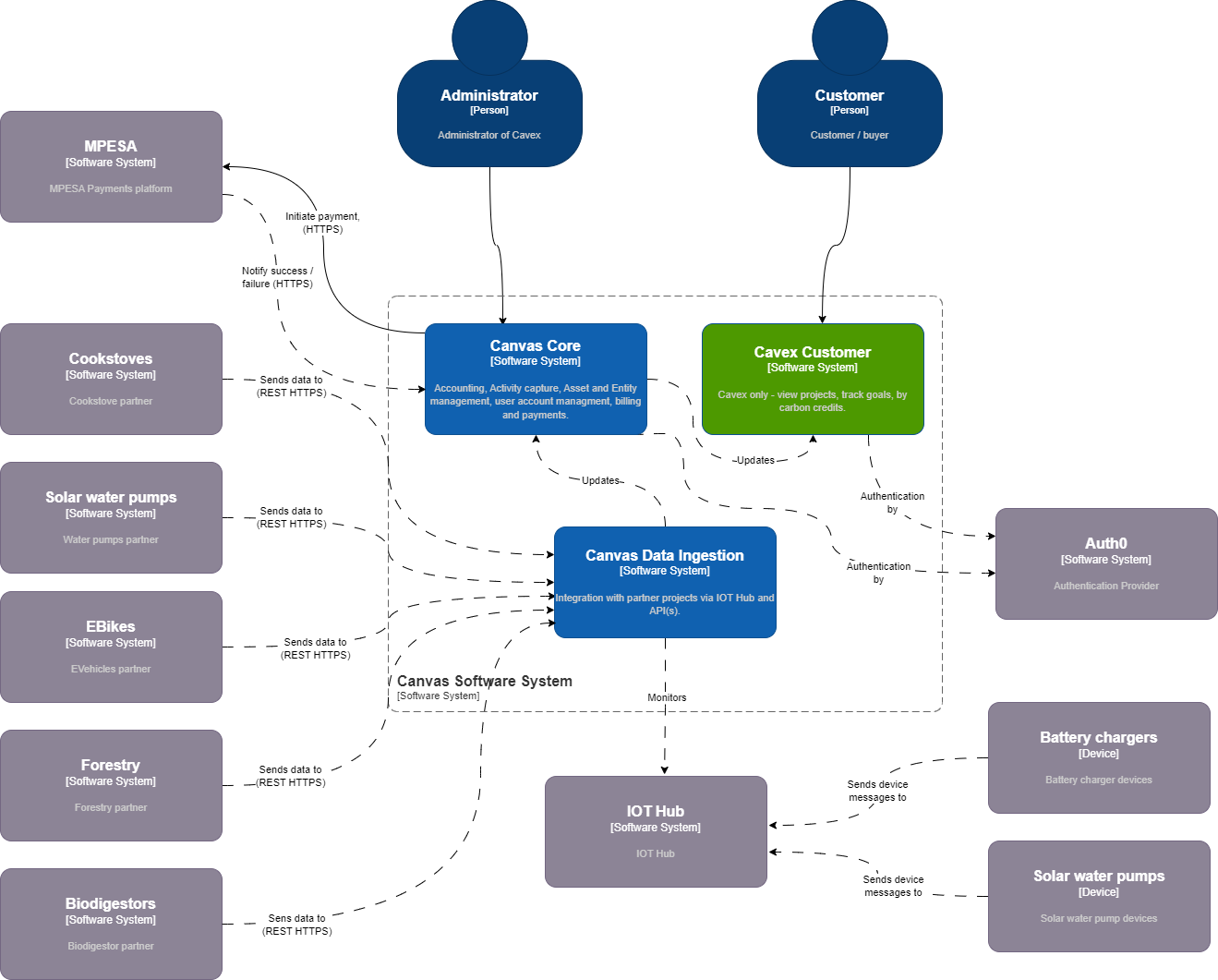
Canvas Container Diagram
The container diagram shows the system with some more implementation detail included. The application landscape is made up of a number of Web apps (ASPNet Core BFF with Angular SPA), some background processors and an internal GRPC services for cross app interactions. Some Azure services including:
Azure SQL
Blob Storadge
Azure IOT Hub
Stream Analytics - work in progress
We are also using Auth0 for Auth.
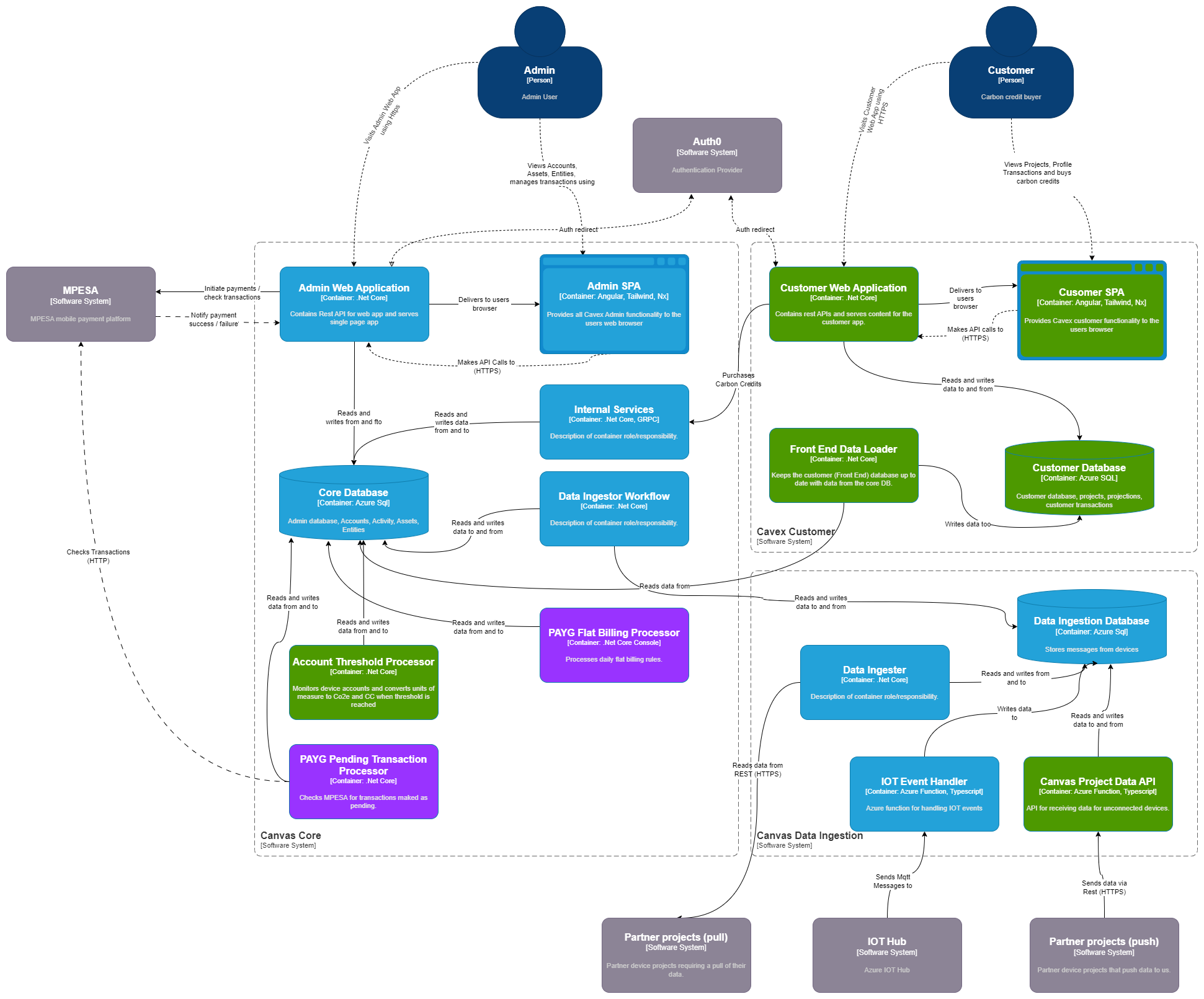
Backend (CORE) Logic Architecture
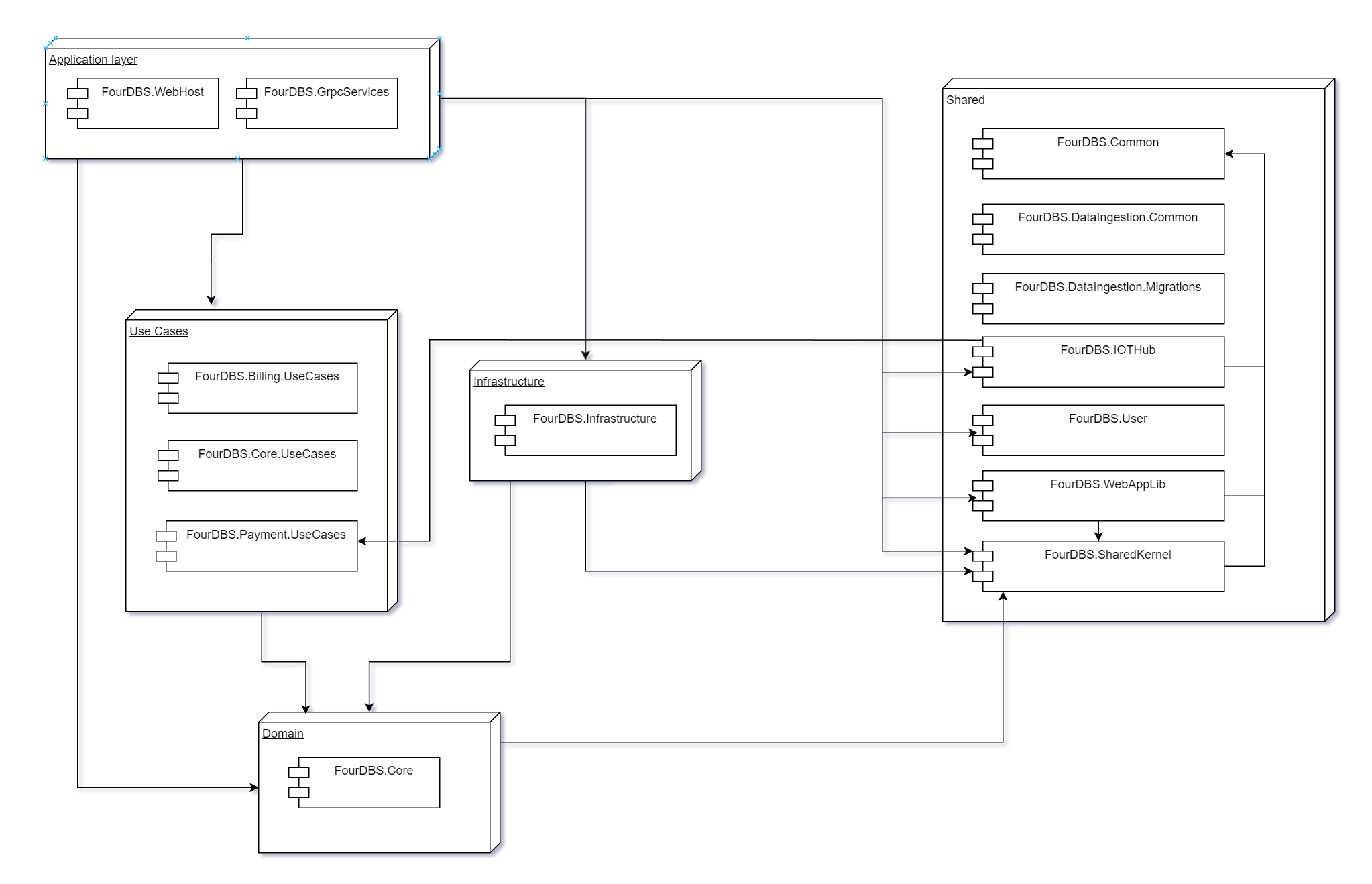
To help clarify the code structure of the CORE part of the Canvas application we have put together a component level diagram. We are using a Clean Architecture Approach alongside some CQRS with Mediatr. The diagram below shows the relationships between the various parts of the backend (CORE) code:
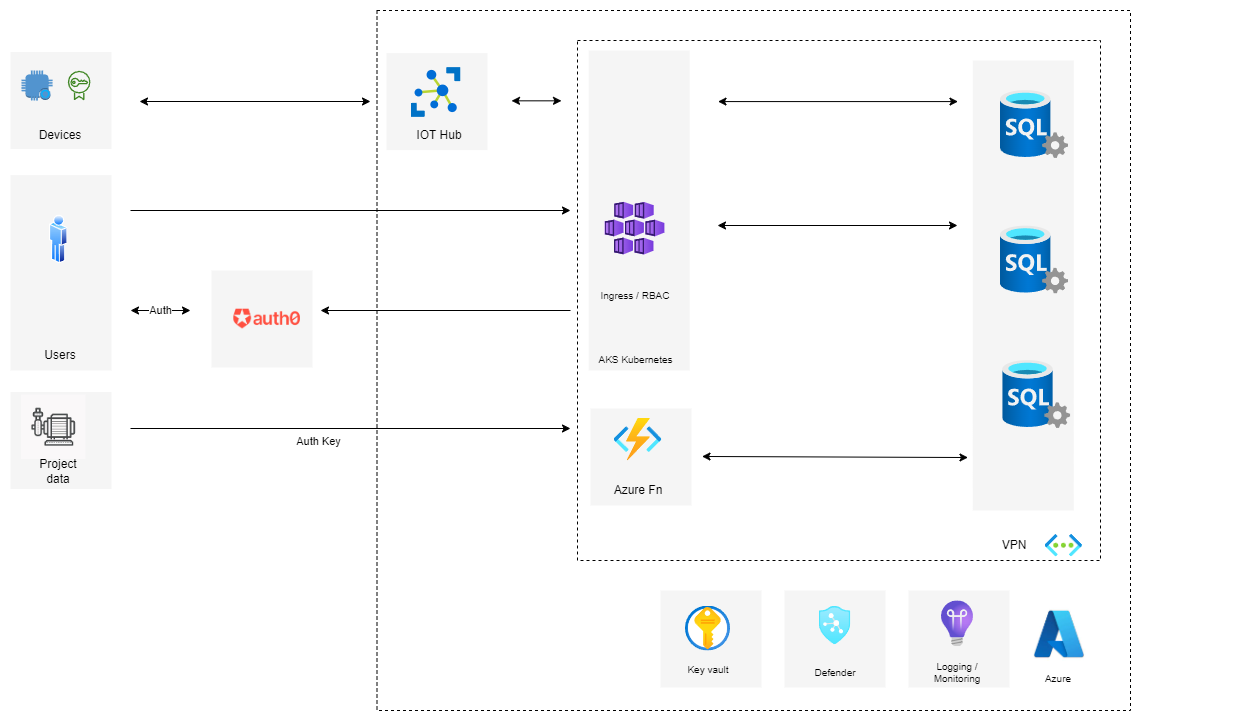
Azure Architecture
The above sections describe how our application is organised in terms of code / components. Below is a diagram showing what this looks like in Azure. All of our c# and angular applications are deployed in a Kubernetes cluster, and we use various Azure services to support them. In particular we are using:
Azure IOT Hub - for managing IOT devices and recording telemetry data.
Azure SQL - for storing our business data
Azure Blob Storage - for storing long term / cold data.
Application Insights - for capturing monitoring / log info.
Auth0 - for Authentication / Authorization
Azure Key Vault - for storing secrets
Defender for Cloud - for monitoring security across the Azure stack.
The current application is shown below:
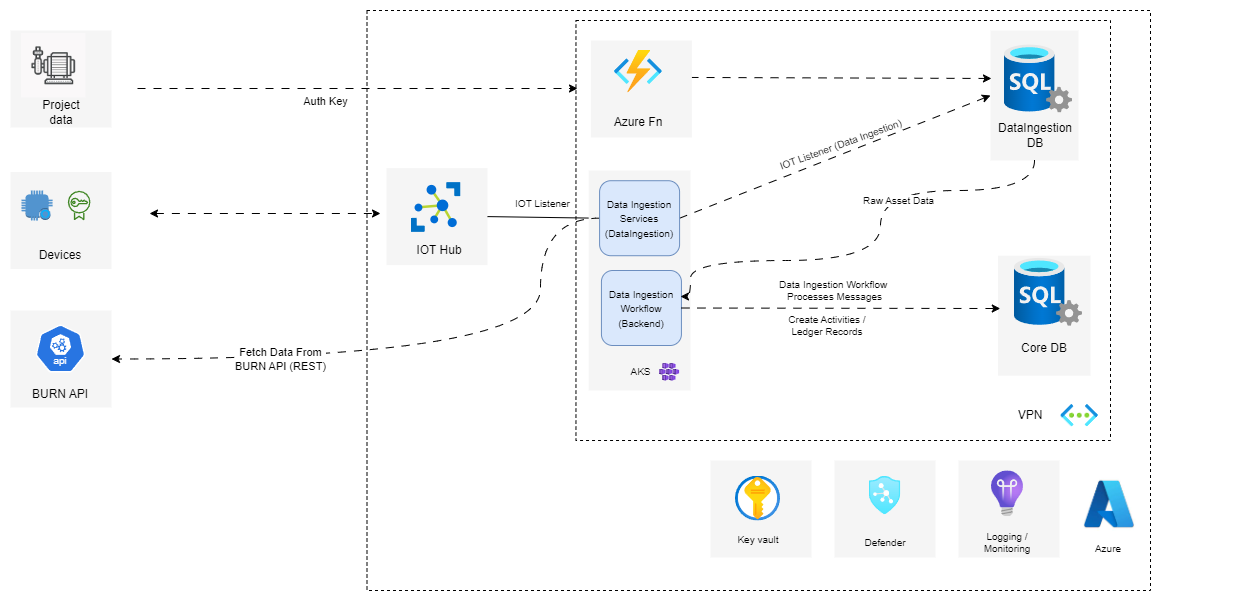
Data Ingestion
As you can see from above, we have separated out our data ingestion logic from the core application services. The data ingestion logic deals with all external interfaces, these currently include:
Azure IOT Hub
Burn API
Canvas Project API (currently and Azure Fn)
The diagram below shows the current Data Ingestion Architecture.
Potential enhancements in the short term:
Azure Stream Analytics - for monitoring / anomoly detection of device telemetry.
Cosmos DB - for short term storage of telemetry data
We are currently evaluating these two and will make a decision on their inclusion shortly.
Background Processing
Across the stack we are using Hangfire to facilitate the running of our background processes. For more info how we do our background processing, see: Canvas Background Processing.